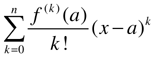
Applied to f(x) = sin x, we find as Taylor polynomial of degree 3 around 0: 0+1*x-0,166666666666667*x^3
Graphically, this gives:
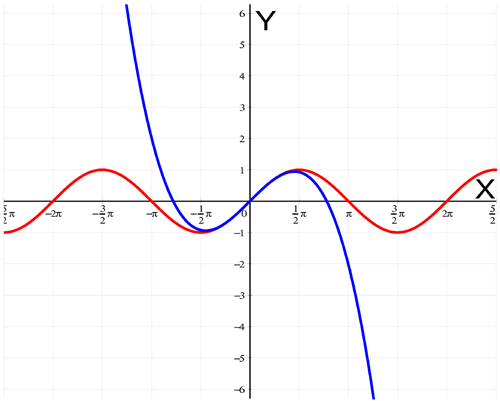
In particular the Taylor polynomial of degree 1 around a is the equation of the straight line tangent to the graph of f in a. This illustrates clearly that the straight line tangent to a curve in a is a linear approximation of the curve. As the degree of the Taylor polynomial increases, the graph of the Taylor polynomial will approximate the graph of f around a better, at least if there is convergence. Below, we see the straight line tangent to the graph of the sine function in the origin, found using the Taylor expansion of degree 1 around 0: